
Ubuntu with GUI Desktop
Table of Content
Launch and Configure Ubuntu with GUI Desktop
Connect to GUI (RDP and VNC)
Connect to your instance via SSH
Deploy files to your VM remotely
Configure GUI
Troubleshooting
Launch and Configure Ubuntu with GUI Desktop
Go to our listing page on Azure Marketplace:
- Ubuntu 18.04 with GUI Desktop
- Ubuntu 20.04 with GUI Desktop
- Ubuntu 22.04 with GUI Desktop
- Ubuntu 24.04 with GUI Desktop
Click on 'Get it now' to initiate the launch dialogue.
Enter a username. Please note that using one of the following reserved keywords will lead to a non-functional GUI: root, daemon, bin, sys, sync, games, man, lp, mail, news, uucp, proxy, www-data, backup, list, irc, _apt, nobody, systemd-network, uuidd, messagebus, systemd-resolve, tcpdump, _chrony, sshd, polkitd, rtkit, avahi, lightdm, pulse, saned, colord, xrdp, gnats, syslog, lxd, dnsmasq, landscape, pollinate, usbmux, systemd-timesync, tss, systemd-coredump, cups-pk-helper, geoclue, gdm, fwupd-refresh
Review the settings and create the virtual machine.
Optional: By default, the VM network ports for SSH, RDP and VNC are open to the public. You can restrict access (e.g., only allow access from your local IP address) under selected VM -> Network settings.
Connect to your Linux VM with RDP or VNC
To access your virtual machine using RDP or VNC, you will need the public IP address and password for the connection. Both can be found on your virtual machine's overview page:
IP Address: Displayed on the overview page for quick access.
RDP/VNC Password: By default, this is the virtual machine name you set at launch.

Open 'Remote Desktop Connection' and connect using the public IP address of your virtual machine.
Important: Expand "More Options" and select "Allow me to save credentials" to ensure the Remote Desktop Connection prompts you for a password before connecting.

When prompted, enter the password (which is the virtual machine name by default).
If you see the screen below, the login attempt has failed, usually due to an incorrect password. You can re-enter the password on this screen, but please note that it uses a virtual English keyboard layout. Special characters may appear differently, as your physical keyboard layout could map them to other symbols. We recommend setting the password directly in the RDP client (refer to the section above).

Connect to your Linux VM via SSH
Please refer to the official documentation for detailed instructions on how to connect to a virtual machine with SSH.
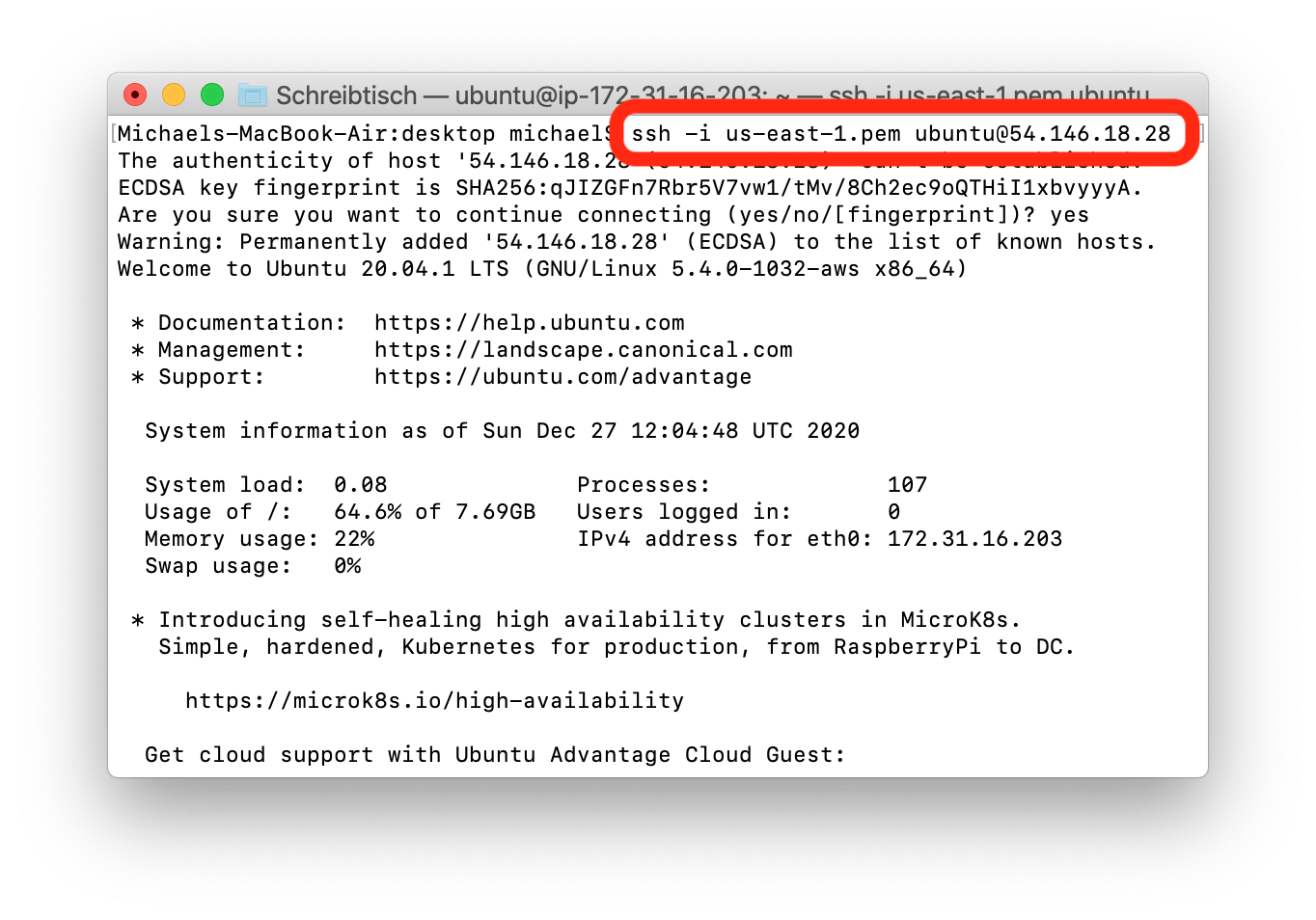
Open a Command Prompt / Terminal window and navigate to the directory where you have saved the .pem key file, which was created in the Azure portal. You can connect to your VM using the username specified during the virtual machine creation process by executing the following command:
ssh -i <name-of-key-file.pem> <username>@<public-ip>
Deploy files on your VM remotely
Download and install WinSCP or any other SCP client of your choice.
Choose 'SFTP' as the file protocol and enter the public IP address of your instance, along with the username you specified when launching the virtual machine.
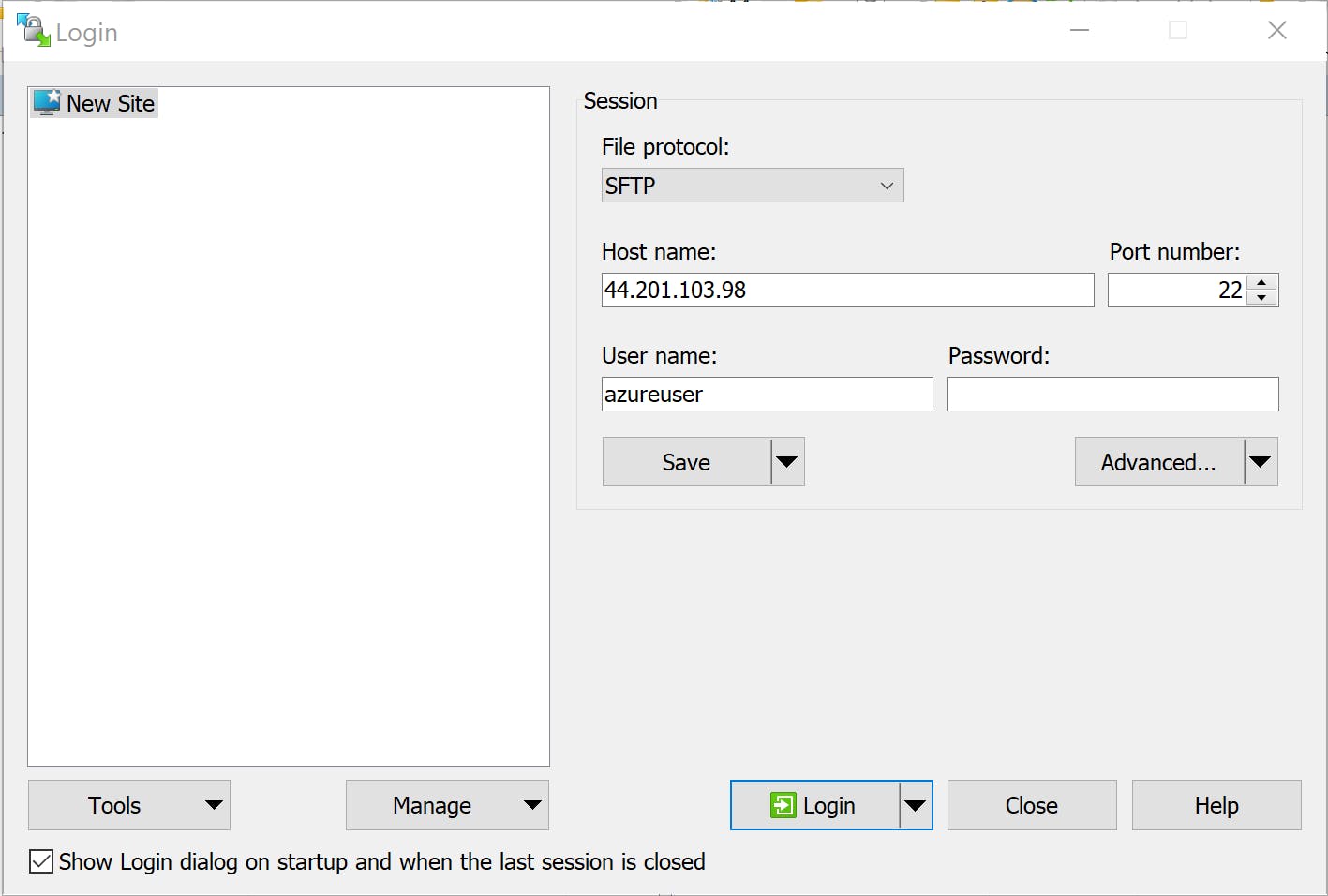
If you opted for password authentication, enter the specified password. Alternatively, if you wish to use a private key file (.pem) that you generated, you can add it by first clicking 'Advanced' and then selecting 'Authentication' from the left-side menu.
Connect to the virtual machine by clicking on 'Login'.
Configure GUI
The script that launches the GUI on every reboot is centrally located at /home/start-gui.sh. You can configure it with:
nano /home/start-gui.sh
The script is executed by a cron job as the root user. You can modify the cron job with:
sudo crontab -e
Change Password for the GUI Session:
To change the password for the GUI session, edit the start-gui.sh file and modify the password variable as desired. Then, reboot the instance. Please note that the password for the GUI session is different from the password for the Linux user.
Use Another User for the GUI Session:
To use a different user for the GUI session, create a new user with:
sudo adduser guiuser
Then, add the user to the sudo group with:
sudo usermod -aG sudo guiuser
Next, edit the start-gui.sh file, change the username variable, and reboot the instance.
Troubleshooting
Resolving RDP/VNC Connection Issues
Potential solutions to resolve your connection issues are:
- Ensure that you are using the correct login credentials. As outlined in our "Connect to GUI (RDP and VNC)" section above, the default password for the GUI is the name of the virtual machine you specified at launch.
- The GUI is designed to reconfigure and restart with every instance reboot. Please try restarting your virtual machine to resolve any connection issues. If the connection issues persist and are not resolved by a reboot, you may need to consider deploying a new virtual machine.
- Verify that your local network is not blocking access to ports 3389 (RDP) or 5901 (VNC). Corporate networks, in particular, tend to block these ports. Ensure that your internal network is not blocking these ports before attempting to connect to the instance GUI.
Resolving Copy & Paste Issues
You may experience issues with copying and pasting to and from the virtual machine. Ensure that your local RDP and VNC clients support clipboard sharing. If the keyboard shortcuts for copy and paste do not work, try using right-click to copy or right-click to paste.
"Failed to execute default Web Browser."
Mozilla Firefox might not be set as the default web browser in the GUI. This results in an error when clicking on the browser icon on the desktop.

To resolve this issue, open the "Default Applications" app, select Mozilla Firefox as the default browser, and then click 'Close'.


The GUI Desktop Freezes
If your desktop environment gets stuck or freezes, ensure that your virtual machine has sufficient memory. We recommend using a virtual machine type with at least 4 GB of memory. Additionally, check if you are running low on available disk space, as this could also cause the GUI to freeze.
RDP Only Shows a Login Page
If you see the login page shown below, it means that RDP is unable to connect to the GUI. This can occur if you are using an incorrect password or if there is another issue with the GUI. Ensure that you are entering the correct password, and try rebooting the system to resolve the issue.
Note: The virtual keyboard layout on this login page is set to English. When typing special characters, be aware that they may appear differently in the virtual environment, as your physical keyboard's layout might map these characters to other symbols. We recommend setting the password directly in the RDP client (see the chapter "Connect to GUI").

